Black & Veatch Study Confirms Trina Solar Vertex 660W PV Modules Offer Lowest BOS and LCOE, Reduced by More than 9.3%
- 22/01/24
- Reliability,210 Modules Comprehensive Analysis
Since the launch of Trina Solar’s 600W+ series, world-renowned design institutes and international third-party organizations have evaluated and studied the BOS and LCOE advantages of Vertex modules. Most recently, Black & Veatch, a global independent services provider to solar projects, completed a CAPEX and LCOE assessment comparing the new generation of ultra-high-power 210mm wafer size PV modules (represented by Trina Solar DEG21C.20-660W, DEG19C.20-545W) to wafer size modules of 182mm (Tier 1 generic 182 -535W), 158mm (Trina Solar DEG15VC.20-480W) and 166mm (Trina Solar DEG17MC.20-450W) (Figure 1).
The results show that the 210mm Vertex modules perform the best overall for reducing CAPEX and LCOE among all the module types (Figure 2). The study found that compared to the 166mm 450W module, the 210mm 660W modules reduce both CAPEX and LCOE by more than 9%. Compared to the 182mm 535W modules, the 210mm 660W modules reduce CAPEX up to 4.58% and lower LCOE up to 3.94%. Additionally, Trina Solar’s 158-84 cell piece layout with 480W peak wattage performs better than standard 166-72 cell piece format regarding CAPEX and LCOE savings.
In terms of cost difference, the increased value stems primarily from the reduced BoS (Balance of System) costs. BoS costs are impacted by the module string length, overall module wattage and the number of modules required to meet the constant capacity assumption made throughout the hypothetical projects. A project utilizing a module with a lower wattage will require more modules and therefore have higher BoS costs, including additional costs for acreage, siting, clearing and grading, racking quantity, cabling, and more.
The 210-660W required the least number of modules to reach the hypothetical project capacity of 100MWac (125MWdc), with 88,383 fewer modules needed. This equals savings of up to 32%. Compared with 166-450W modules, the Vertex 210–660W module achieve additional cost-saving benefits across the board of:
- BoS material savings: ~$1.6M
- BoS installation savings: ~$979K
- Rack and Post installation savings: ~$1.8M
- Indirect Construction savings: ~$1.9M
- Administrative and EBT savings: ~1.1M
- Total initial cost CAPEX savings: ~$9.6M
Project Details
Location: Texas, U.S., Latitude: 34.36° Longitude: -99.89°
Annual GHI: 1,865 kWh/m2
Average temperature: 17.5°C
Project size: 100MW
Module Wafer sizes (4): 166 (M6), 158(G1), 182 (M10), 210 (G12)
Module types (5): 166-450W, 158-480W, 182-535W, 210-545W, 210-660W
Method of installation: Nextracker 1P design
Ground coverage ratio (GCR): 0.35
DC/AC ratio: 1.24
Inverter type: Central Inverter: Sungrow SG3600UD-MV
Regular lot shape, flat terrain, no irregular shading.
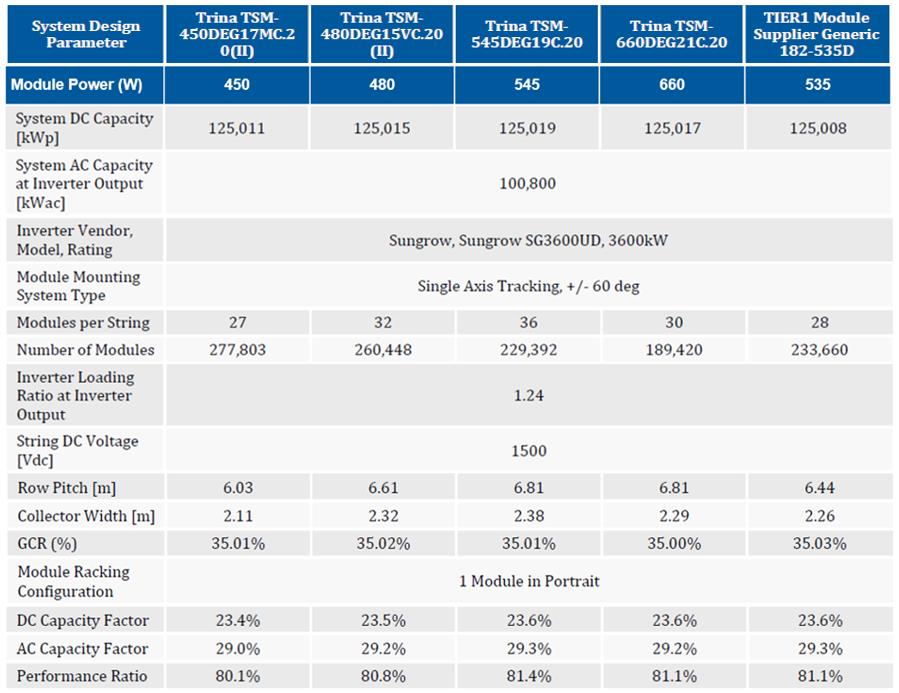
Figure 1: Configuration of the PV Project
Initial Construction Costs, LCOE Comparison
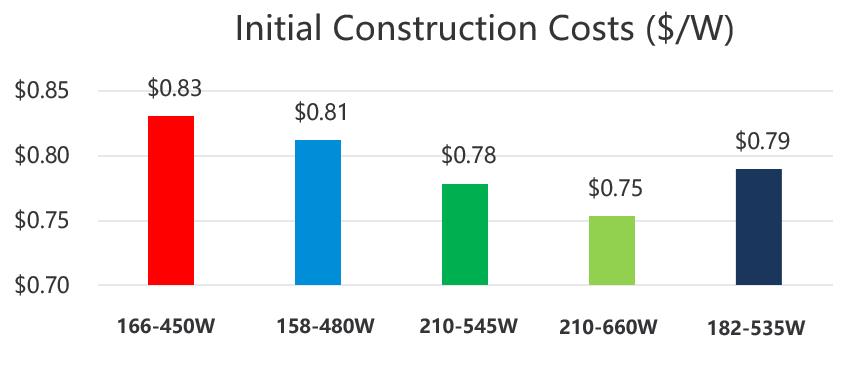
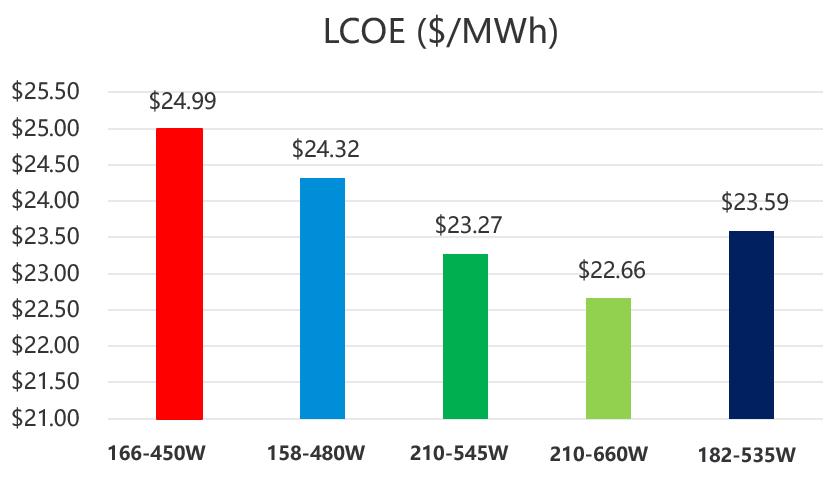
Figure 2: Comparison of Initial construction costs and LCOE
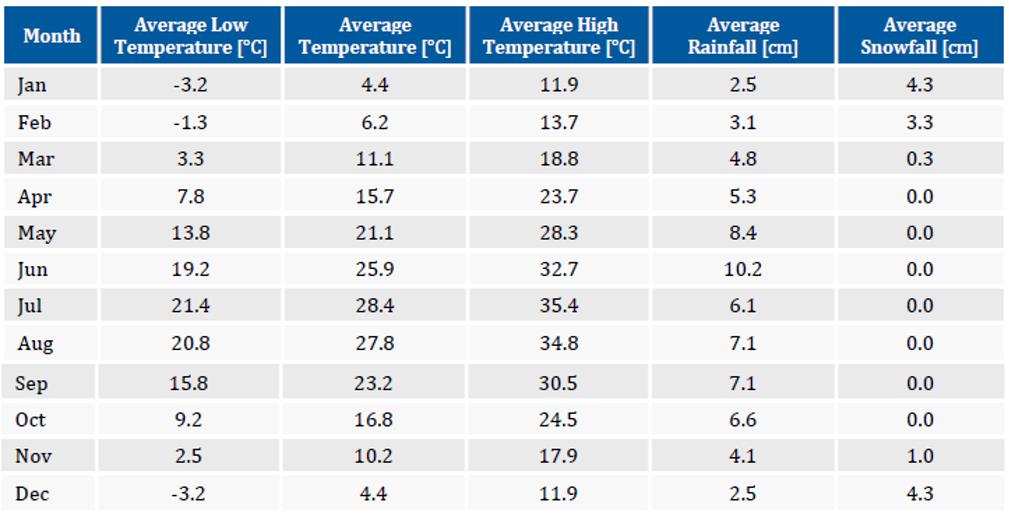
Figure 3: Historic Average Monthly Weather Conditions at the Project Location
About Black & Veatch
Founded in 1915, Black & Veatch is a global employee-owned engineering, procurement, construction (EPC) and consulting company with a 100-year legacy of innovations in sustainable infrastructure. The company specializes in infrastructure development in power, oil and gas, water, telecommunications, government, mining, data centers, smart cities and banking and finance markets.
About Trina Solar
From 2020 to 2021, Trina Solar launched the Vertex 210mm 410W, 510W, 555W, 605W and 670W modules, leading the industry into the new era of 600W+. The Vertex series has been widely recognized by customers globally, opening a new channel to reduce the cost of electricity and guarantee the long-term stable returns of power plants. As the world's leading provider of PV smart energy and energy solutions, Trina Solar is committed to bringing its product advantages into working with global partners to accelerate the global application of smart energy and create a new world of carbon-free energy.
Relevant Topics
Smart Energy Solutions
delivered straight to your inbox


